Heatpipe
Kolink Int'l. Corp. has established a specialized heat pipe production line in Taiwan,
primarily manufacturing heat pipes with outer diameters of D5, D6, and D8mm,
with a maximum monthly production capacity of 500,000 units.
We offer customized production based on customer requirements, allowing
flexible adjustments to heat pipe length, bending angles, and other parameters
to accommodate small-volume, high-variety manufacturing needs.
From copper material selection and production processes to 100% finished product
inspection, we adhere to standardized procedures and utilize advanced
production equipment to ensure stable and reliable quality.

A heat pipe is a sealed chamber with a vacuum-induced negative pressure. When it contacts a heat source, the internal fluid vaporizes, and upon reaching the cooler end, it condenses and returns via the capillary structure. This continuous phase change efficiently transfers heat.
The internal capillary structures of heat pipes come in various types, commonly categorized as follows:
![]() Groove
Heat Pipe
Groove
Heat Pipe
Groove Heat Pipe
The groove heat pipe forms internal grooves during the copper tube extrusion process, which enhances its heat transfer performance in the horizontal direction. However, its performance significantly deteriorates in anti-gravity environments.

![]() Sintered Heat Pipe or Powder Heat Pipe
Sintered Heat Pipe or Powder Heat Pipe
Sintered Heat Pipe (Powder Heat Pipe)
Sintered heat pipe features a uniformly sintered powder layer inside the tube. The appropriate powder type is selected based on different power requirements, and by adjusting the capillary structure and permeability, optimal heat transfer performance is achieved. Due to the capillary structure facilitating fluid transfer, this heat pipe performs exceptionally well in anti-gravity environments.
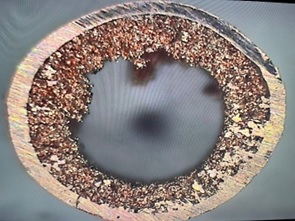
![]() Mesh Heat Pipe or Fiber Heat Pipe
Mesh Heat Pipe or Fiber Heat Pipe
Mesh Heat Pipe
Placing
woven mesh and braided tubes inside the inner tube as a capillary structure
makes the conduction process simpler compared to sintered heat pipes.

![]() Composite Heat Pipe
Composite Heat Pipe
Composite Heat Pipe
Composite heat pipes combine multiple capillary structures, with common combinations including grooved tubes and copper powder sintering. This enhances capillary action and permeability, maximizing thermal performance. Their superior heat transfer capabilities make them especially suitable for high-wattage applications.

